Understanding referrals in health insurance plans is essential for navigating care, saving money, and avoiding denied claims. A referral is a formal approval from your primary care doctor allowing you to see a specialist or receive certain services.
Knowing how referrals in health insurance plans work helps you understand your network rules, manage costs, and make informed healthcare decisions. Platforms like 👉 QuoteMaestro allow you to compare plans and see which require referrals for specialty care.
What Is a Referral in Health Insurance Plans?
A referral is a written or electronic request from your primary care provider (PCP) authorizing you to see a specialist.
-
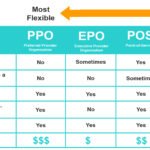
Who needs a referral? Typically, HMO and some POS plans require referrals.
-
Who doesn’t? PPO and some HDHP plans often allow you to see specialists without a referral, though costs may differ.
Referrals are used to ensure your care is medically necessary and coordinated, keeping costs manageable for both you and your insurance provider.

Why Referrals Are Required
Insurance plans may require referrals for several reasons:
-
To manage costs and avoid unnecessary specialist visits
-
To ensure coordinated care with your primary doctor
-
To track treatment progress and outcomes
-
To comply with plan rules for in-network care
Understanding referrals in health insurance plans helps you avoid denied claims and unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.

How to Get a Referral
-
Schedule a visit with your primary care provider (PCP).
-
Explain why you need to see a specialist.
-
Your PCP submits the referral electronically or provides a written form.
-
Confirm with your insurance plan that the referral is approved before the specialist visit.
Tools like 👉 QuoteMaestro can help you compare insurance plans to see which require referrals and which allow self-referral to specialists.
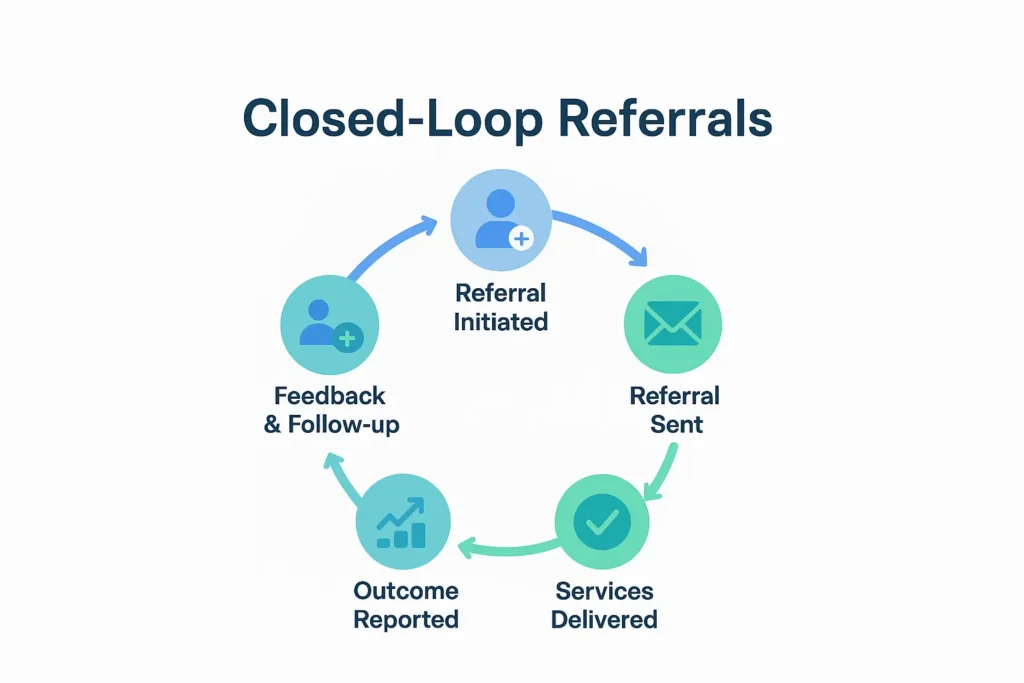
Types of Referrals
-
Standard Referral: PCP approval needed before seeing a specialist.
-
Urgent Referral: For urgent medical needs, your PCP can expedite approval.
-
Self-Referral: Some plans, like PPOs, allow patients to see specialists without PCP approval, though copays may vary.
Costs and Coverage Considerations
-
HMO plans: Almost always require referrals; out-of-network visits usually aren’t covered without a referral.
-
PPO plans: Referrals may not be needed, but seeing out-of-network specialists can increase costs.
-
POS plans: Hybrid plans may require referrals for certain services.
Using a platform like 👉 QuoteMaestro helps you compare plans and choose one that balances referral requirements with flexibility and cost.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Skipping the referral and assuming the specialist visit is covered.
-
Choosing out-of-network providers without confirming coverage.
-
Not checking if urgent referrals require prior authorization.
-
Forgetting to renew or update referrals if your treatment extends.
Understanding referrals in health insurance plans ensures smooth access to care without unexpected bills.

FAQs: Referrals in Health Insurance Plans
What is a referral in a health insurance plan?
A referral is approval from your PCP to see a specialist or receive certain services.
Do all health insurance plans require referrals?
No. HMO and POS plans often require referrals, while PPO plans typically do not.
Can I see a specialist without a referral?
It depends on your plan. Using platforms like 👉 QuoteMaestro helps you find plans that allow self-referrals.
Does a referral affect costs?
Yes. Using a specialist without a required referral may lead to higher copays or denied coverage.
How long is a referral valid?
It depends on the plan and type of service. Some referrals are for a single visit, others for multiple visits or ongoing treatment.
Final Thoughts
Understanding referrals in health insurance plans is essential to avoid denied claims, reduce out-of-pocket costs, and ensure coordinated care. By knowing when you need a referral and how to obtain one, you can navigate your healthcare efficiently.
Compare insurance plans using platforms like 👉 QuoteMaestro to find plans that fit your needs, including referral requirements, coverage, and in-network flexibility.